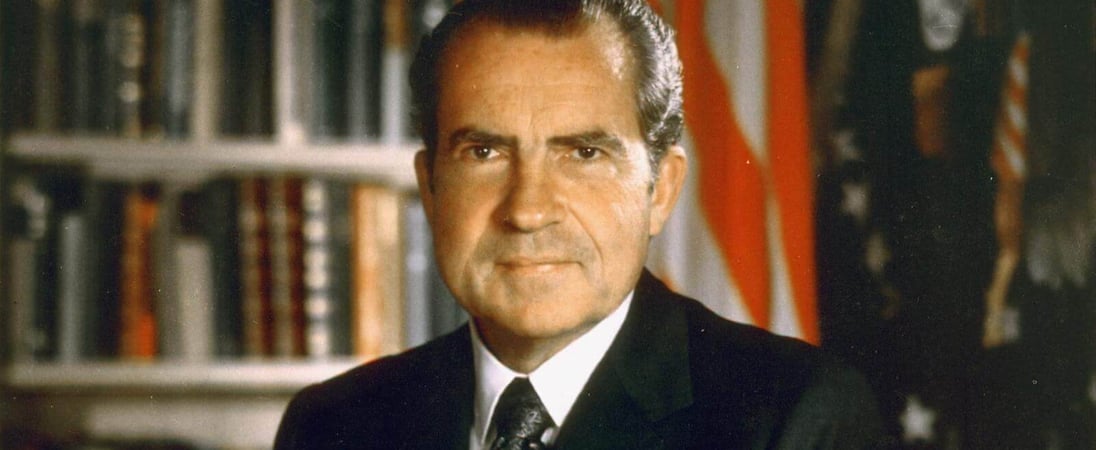
Richard Nixon's birthday
Step into the world of Richard Nixon, the 37th President of the United States. From his rise to power to his controversial downfall, his story is a fascinating tale of ambition, scandal, and political deception. Let’s dive into the life and legacy of one of America’s most polarizing figures.
Born in Yorba Linda, California in 1913, Richard Milhous Nixon grew up in a Quaker household and had a strict upbringing, and went on to graduate from Whittier College and Duke University School of Law. He began his political career in the 1940s, serving as a member of the House of Representatives and later as a Senator from California, and became known for his aggressive tactics during the House Un-American Activities Committee, which investigated alleged communist influence in the government and entertainment industry.
In 1952, Nixon was chosen as Dwight D. Eisenhower’s running mate and they were elected as President and Vice President of the United States. As Vice President, Nixon played a significant role in foreign policy, including the establishment of diplomatic relations with China and the handling of the Cuban Missile Crisis.
In 1968, Nixon ran for president and won the election. As president, he implemented policies such as the creation of the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and the establishment of the “Nixon Doctrine”, which aimed to reduce the US’s involvement in the Vietnam War. However, his presidency was plagued by scandal, most notably the Watergate scandal, which led to his resignation in 1974, becoming the first president in US history to do so.
After his presidency, Nixon retired from public life and wrote several books, including “RN: The Memoirs of Richard Nixon” (1978) and “The Real War” (1980). Nixon passed away in 1994 at his home in Park Ridge, New Jersey, at 81 years of age.
Richard Nixon Timeline
Richard Nixon is remembered as a complex and polarizing figure in American history. He rose to power as a fierce anti-communist during the Cold War and played a key role in shaping foreign policy, as well as domestic policies. However, the Watergate scandal and its aftermath had a negative effect on his legacy and the presidency as a whole. Despite his accomplishments, he is also remembered for the controversies of his presidency, which overshadowed his contributions to American history.
Richard Nixon FAQs
What is the Watergate scandal?
During Richard Nixon’s administration, there was a political outrage that became commonly known as The Watergate Scandal. It involved the break-in of the Democratic National Committee headquarters at the Watergate office complex in Washington D.C. in 1972 and the subsequent cover-up of the administration’s involvement by Nixon and his administration. This resulted in several high-ranking officials being convicted of charges related to the break-in and cover-up, and eventually led to the resignation of Nixon in 1974.[1]
What were some of Richard Nixon’s domestic policies?
As President, Nixon implemented several domestic policies including the Environmental Protection Agency, which aimed to protect the environment and improve air and water quality. He also created the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) to ensure safe and healthy working conditions for Americans. Additionally, Nixon signed the Clean Air Act and the Clean Water Act.[2]
What was the “Nixon Doctrine”?
The “Nixon Doctrine” was a foreign policy strategy that sought to mitigate US engagement in the Vietnam conflict and instead, rely on local allies to fight their own wars. The doctrine planned to lessen the US’s role as the world’s police and instead, focus on strengthening the capabilities of allies to defend themselves.[3]
Also on this date...
National Word Nerd Day
Lexophiles rejoice! People who love words find joy in expanding their vocabulary, playing word games, and creating witty puns.
National Cassoulet Day
A French slow-cooked casserole loaded with savory meat, tender beans, and fragrant herbs - perfect for chilly nights.
International Choreographers Day
International Choreographers Day is here to pay attention to and show appreciation for those people who help the rest of the world enjoy, share in and be entertained by dance.
National Law Enforcement Appreciation Day
Dedicated to safeguarding communities, these individuals uphold justice with unwavering commitment, embodying the essence of duty and honor.